Gun Control Movement
Movement Breakdown
The Gun Control Movement in the United States stands as a complex and deeply rooted debate, intricately woven into the fabric of the nation's history and legal framework. Since the Second Amendment's ratification in 1791, which codified the right to bear arms, the discourse has evolved, influenced by significant events and critical Supreme Court decisions such as United States v. Miller (1939) and District of Columbia v. Heller (2008). These landmark cases underscored the individual's right to own firearms for lawful purposes, including self-defense at home, setting the stage for ongoing discussions around the balance between gun rights and regulation.
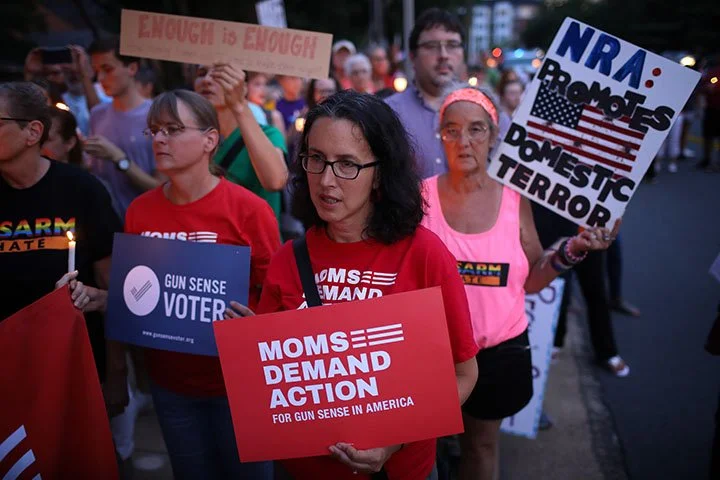
At the heart of this debate are potent figures and organizations, spanning from legislators and the influential National Rifle Association (NRA) to advocacy groups advocating for tighter gun control, such as Everytown for Gun Safety. The NRA's longstanding resistance to gun control contrasts with the efforts of other entities and individuals, particularly those affected by gun violence, who call for more stringent regulatory measures. The United States' struggle with gun-related violence is characterized by alarmingly frequent mass shootings and elevated gun-related homicide rates, driving demands for comprehensive solutions like universal background checks and restrictions on specific types of firearms, especially assault rifles.
Advocates for gun control argue for immediate action to curtail the accessibility of firearms, emphasizing the critical link between the country's mental health crisis and gun violence. This intersection of widespread mental health issues and the easy availability of guns highlights the need for holistic approaches that combine gun regulation with improved mental health services. On the other side, gun control opponents believe that such restrictions infringe on freedoms enshrined in the Second Amendment. They suggest that enhancing existing laws and promoting a culture of responsible gun ownership through better safety training and education could reduce gun violence risks without necessitating new regulations.
Communities Affected
Communities affected by the gun control movement in the United States encompass a broad spectrum, including urban areas plagued by gun violence, rural communities where firearms are deeply ingrained in the culture, and suburban neighborhoods where safety concerns intersect with debates over Second Amendment rights. In recent years, many schools have been targeted, raising concerns about the safety of children in their place of education.
Major Issues of Those Affected By Gun Violence
Gun Violence Epidemic: Urban communities disproportionately experience the devastating impact of gun violence, with high rates of shootings, homicides, and gang-related activities. This issue not only leads to loss of life but also contributes to a climate of fear and trauma within these neighborhoods.
Mass Shootings: The prevalence of mass shootings in public spaces, including schools, places of worship, and entertainment venues, has garnered widespread attention and sparked national debates about gun control measures. These tragic events leave lasting scars on affected communities and prompt calls for stricter regulations on firearm access.
Domestic Violence: Firearms play a significant role in cases of domestic violence, with lethal consequences for victims. Access to firearms increases the risk of intimate partner homicide, making it a pressing concern for communities grappling with issues of gender-based violence.
Suicide Prevention: Access to firearms is a significant risk factor for suicide, particularly among vulnerable populations such as veterans and LGBTQ+ individuals. Communities must address the intersection of mental health and gun access to prevent the tragic loss of life through suicide.
Child Safety: Accidental shootings involving children highlight the need for safe storage practices and regulations to prevent unauthorized access to firearms. Communities must prioritize initiatives that promote responsible gun ownership and minimize the risk of unintentional harm to children.
Social Leaders of The Movement
Shannon Watts
Founder of Moms Demand Action for Gun Sense in America
Gabrielle Giffords
Former US Representative, Founder of Giffords
Warren Buffett
The chairman and CEO of Berkshire Hathaway has also been involved in funding efforts to address gun violence. Through his philanthropic contributions, Buffett has supported organizations working to implement gun control measures and reduce the impact of firearms on communities across the country.
Emma González
A survivor of the 2018 Marjory Stoneman Douglas HS shooting in Parkland, Florida and Gun Control Advocate
Political Leaders of The Movement
Economic Leaders of The Movement
Michael Bloomberg
As a billionaire philanthropist and former mayor of New York City, Michael Bloomberg has been a significant financial supporter of efforts to combat gun violence. He co-founded Everytown for Gun Safety, one of the largest gun control advocacy organizations in the United States. He has provided significant funding for various initiatives promoting gun safety laws.
Barack Obama
44th President of the United States, Barack Obama, made gun control a key issue during his presidency, advocating for measures such as expanded background checks and an assault weapon.s ban in response to mass shootings.
Cory Booker
US Senator Cory Booker has been a prominent advocate for gun control, sponsoring legislation to strengthen background checks and ban assault weapons. He has been vocal about the need for comprehensive gun reform to address the epidemic of gun violence.
President Joe Biden
46th President of the United States, Joe Biden, has long advocated for gun control. He has supported policies aimed at reducing gun violence, including universal background checks and a ban on assault weapons.
Chuck Schumer
NY Senator and Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer has been a vocal proponent of gun control legislation, advocating for measures to prevent gun violence and enhance public safety.
Lucy McBath
Gun Control Activist and former national spokesperson for Everytown for Gun Safety, former US Representative for Georgia's 6th congressional district
Nancy Pelosi
Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, Nancy Pelosi, has been a staunch supporter of gun control measures. Under her leadership, the House has passed several bills to strengthen background checks and close loopholes in gun laws.
Kamala Harris
US Vice President Kamala Harris has supported gun control measures throughout her political career. As a senator, she co-sponsored legislation for universal background checks and has continued to advocate for gun safety measures at the federal level.
Tom Steyer
A billionaire investor and philanthropist has allocated resources to support initiatives to prevent gun violence. His philanthropic foundation has funded research, advocacy campaigns, and community-based programs focused on promoting gun safety and reducing gun-related harm.
David Hogg
A survivor of the 2018 Marjory Stoneman Douglas HS shooting in Parkland, Florida, Co-founder of March For Our Lives
Fred Guttenberg
Father of daughter who lost their life in the Parkland school shooting, and Gun Saftey Advocate
Community Organizations Involved
Forward Movements
Enactment of Background Check Systems: The Brady Handgun Violence Prevention Act of 1993 established the National Instant Criminal Background Check System (NICS), requiring federal background checks on firearm purchasers in the United States, representing a significant policy win for gun control advocates.
Assault Weapons Ban of 1994: The Federal Assault Weapons Ban, enacted in 1994 as part of the Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act, prohibited the manufacture for civilian use of certain semi-automatic firearms and large-capacity magazines for a decade until its expiration in 2004.
State-Level Legislation: Various states have enacted their gun control measures, such as California's robust firearm regulations, including bans on certain assault weapons, background checks for all firearms sales, and red flag laws that allow for the temporary removal of firearms from individuals deemed a threat to themselves or others.
Public Opinion and Activism: Following mass shootings, there has been a noticeable increase in public activism and support for gun control measures, exemplified by movements like March for Our Lives, which emerged after the Parkland school shooting in 2018. This activism has influenced public opinion and, in some cases, policy discussions at various government levels.
Setbacks
Expiration of the Assault Weapons Ban in 2004: The Federal Assault Weapons Ban expired in 2004, and attempts to renew it have consistently failed, reflecting a significant setback for gun control advocates who argue that such weapons disproportionately contribute to the lethality of mass shootings.
Supreme Court Rulings: Decisions like District of Columbia v. Heller (2008) and McDonald v. City of Chicago (2010) have reinforced the Second Amendment's protection of an individual's right to keep and bear arms, challenging and sometimes overturning gun control measures.
Legislative Stalemates at the Federal Level: Despite periodic pushes for new gun control laws, especially after high-profile mass shootings, the U.S. Congress has often been deadlocked on gun legislation, reflecting deep political and ideological divides on this issue.
Rise of "Constitutional Carry" Laws: A growing number of states have passed "Constitutional Carry" laws, allowing citizens to carry firearms openly or concealed without a permit, reflecting a significant setback for the gun control movement which advocates for stricter regulations on who can carry firearms publicly.
Ways To Support
Engage with and support organizations that align with your stance on gun control, whether advocating for stricter laws or protecting gun rights. Joining their efforts can amplify the impact through numbers and collective action.
Participate in community and legislative processes to voice your opinion and effect change. This can include attending town hall meetings, writing to your representatives, and participating in local advocacy groups.
Educate yourself and others on the complexities of gun legislation and the impacts of gun violence on communities. Knowledge is power, and informed citizens can make compelling arguments for change.
Support victims and communities affected by gun violence through volunteering, fundraising, and awareness campaigns. This not only aids those directly impacted but also strengthens the community's resolve against gun violence.
Leverage social media and digital platforms to spread awareness and advocate for gun control measures. The digital landscape offers a vast audience and can be a powerful tool for mobilizing legislative change support.
Learn More
President Joe Biden to Establish First-Ever White House Office of Gun Violence Prevention, To Be Overseen by Vice President Kamala Harris | White House
After years of little progress, Texas gun control and safety advocates see some small openings for dialogue at the Capitol | The Texas Tribune
AMA advocates to prevent gun violence and to increase gun safety | AMA
Relevant Hashtags
#GunControlNow, #EndGunViolence, #MarchForOurLives, #NeverAgain, #SafeSchools